工厂模式
工厂模式是Java中最常用的设计模式之一,这种类型的设计模式属于创建型模式,它提供了一种创建对象的最佳方式。在工厂模式中,我们在创建对象时不会对客户端暴露创建逻辑,并且是通过使用一个共同的接口来指向新创建的对象。
个人认为工厂模式就是为了隐藏对象的具体实现,提供一个接口给用户使用,这个接口就是工厂,就想我们买一件产品,我们可以直接向工厂批发,我们只需要提供给厂家产品的名字,厂家就提供给我们可以完成我们需求的对应的产品。这就是工厂模式,我们并不需要知道这个产品的原材料是什么、是怎么做出来的。
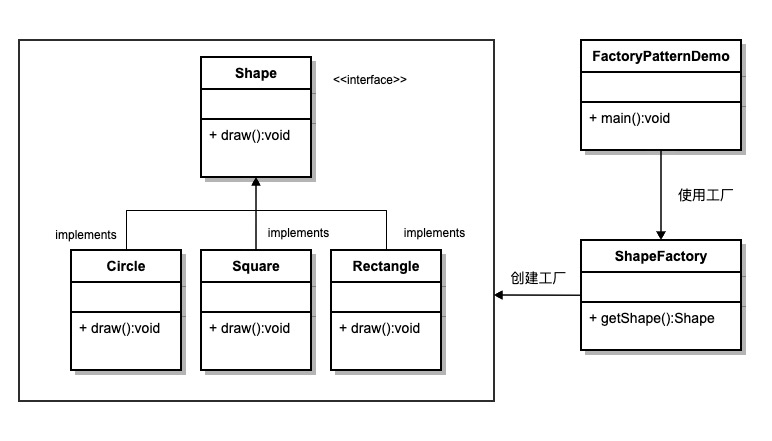
下面的图诠释了工厂模式的工作流程
步骤 1
创建一个接口:
1
2
3
4
| Shape.java
public interface Shape {
void draw();
}
|
步骤 2
创建实现接口的实体类。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| Rectangle.java
public class Rectangle implements Shape {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle::draw() method.");
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| Square.java
public class Square implements Shape {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Square::draw() method.");
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| Circle.java
public class Circle implements Shape {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Circle::draw() method.");
}
}
|
步骤 3
创建一个工厂,生成基于给定信息的实体类的对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| ShapeFactory.java
public class ShapeFactory {
public Shape getShape(String shapeType){
if(shapeType == null){
return null;
}
if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("CIRCLE")){
return new Circle();
} else if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("RECTANGLE")){
return new Rectangle();
} else if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("SQUARE")){
return new Square();
}
return null;
}
}
|
步骤 4
使用该工厂,通过传递类型信息来获取实体类的对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| FactoryPatternDemo.java
public class FactoryPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShapeFactory shapeFactory = new ShapeFactory();
Shape shape1 = shapeFactory.getShape("CIRCLE");
shape1.draw();
Shape shape2 = shapeFactory.getShape("RECTANGLE");
shape2.draw();
Shape shape3 = shapeFactory.getShape("SQUARE");
shape3.draw();
}
}
|
步骤 5
执行程序,输出结果:
1
2
3
| Inside Circle::draw() method.
Inside Rectangle::draw() method.
Inside Square::draw() method.
|


